AI Agents are shaping technological trends, marked by milestones such as the launch of Astra during Google I/O 2023 or the emergence of GPT-4o. Major corporations are investing billions of USD in this technology to automate processes and optimize efficiency. In this article, FPT.AI will guide you in exploring how AI Agents are helping businesses improve workflows, enhance customer experiences, and optimize operational activities.
What are AI Agents? The Fundamental Components of an AI Agent
AI Agents are Artificial Intelligence (AI) models and algorithms capable of interacting with the environment and making decisions in the real world without needing any instructions or task direction from humans.
In other words, AI Agents are personal assistants designed to emulate human intelligence. They rely on AI technologies such as Machine Learning (ML) and Natural Language Processing (NLP) to process and analyze data, as well as execute actions based on users’ requests and preferences.
An AI Agent can process information, make decisions, and perform actions to interact with related conditions and systems. AI Agents can be applied in various fields, ranging from virtual customer assistants to complex automated control systems, or even robots operating in real-world environments.

Differences between AI Agents and AI Chatbots
Below is a comparison table highlighting the distinctions between AI Agents and AI Chatbots:
| Criteria | AI Agent | AI Chatbot |
| Primary Purpose | Executes automated and independent tasks, often without human interaction | Interacts with humans, primarily for customer support or answering questions |
| Automation Capability | Fully automates tasks without human intervention | Lacks full automation capability, relying on human interaction |
| Human Interaction | May not require human interaction during operation | Mainly interacts with humans via text or voice |
| Form | Can be software, physical robots, or smart home devices (e.g., vacuum robots, smart thermostats) | Primarily exists as text or voice-based interfaces (chat applications, chatbots, or virtual assistants) |
| Task Processing Ability | Capable of handling complex tasks like automation and data-driven decision-making | Limited to basic questions and answers, with less capability for handling complex tasks |
| Application Scope | Broad, applicable in various domains such as automation, medical diagnostics, and personal finance | Primarily in customer support, answering queries, and chat-based interactions |
| Response Mechanism | Proactive and reactive to the environment, capable of planning and complex decision-making | Reacts based on predefined scripts and dialogue models, often limited in contextual understanding |
| Learning Capability | Continuously learns and adapts based on feedback from the environment and other agents | Typically lacks continuous learning ability; updates are manual |
| Context Processing | Deep understanding of context and emotions, capable of processing social signals and complex scenarios | Relies on fixed scripts, struggles with non-standard requests |
| Example Applications | Robotic vacuum cleaners, business automation systems, smart thermostats, personal financial assistants | Customer support chatbots on websites, virtual assistants like Siri or Google Assistant |
How do AI agents work?
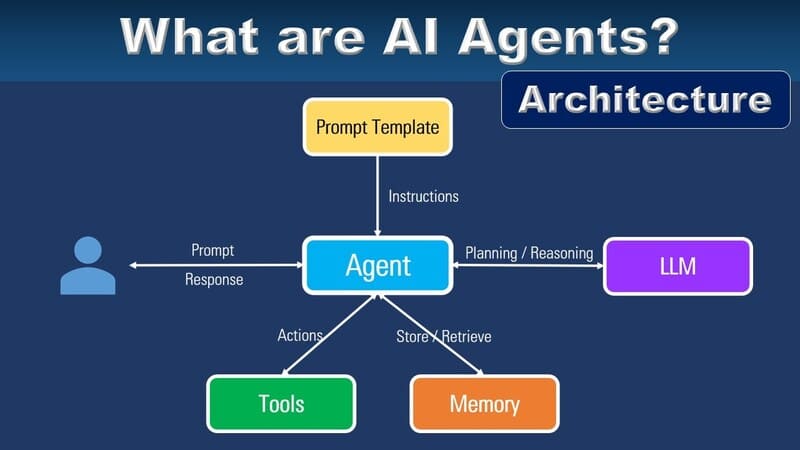
When receiving a command (goal) from the user (Prompt), AI Agents plan and break the goal into smaller, actionable tasks.
- Perception and Data Collection: During execution, using sensors, AI Agents gather information (e.g., transaction data, customer interaction history) from various sources, including external datasets, web searches, APIs, and even other agents. This data collection process ensures the agents continuously update their knowledge base, self-adjust, and fix errors if necessary. Advanced AI Agents can integrate and process real-time data, ensuring they have the most up-to-date information to handle queries effectively.
- Processing and Decision-Making: The processors of AI Agents utilize algorithms, deep neural networks, machine learning models, and artificial intelligence to analyze the gathered information and determine the necessary actions. For example, they can identify the most suitable response to a customer query by analyzing past interactions and the current context. This decision-making process is enhanced by their ability to learn from previous experiences, refining their responses over time.
- Action Execution: After making a decision, AI Agents take the required actions. This can include responding to customer queries, processing requests, or escalating complex issues to a human agent. The execution is designed to be seamless and efficient, ensuring customers receive timely and accurate responses.
- Learning and Adaptation: Throughout the process, the memory of AI Agents continuously stores information (e.g., decision histories or learned rules), enabling them to reference, adjust actions, and improve performance over time. AI Agents continuously learn from each interaction, fine-tuning their algorithms to enhance accuracy and efficiency. They update their knowledge base and leverage feedback to improve future interactions. This continuous learning ensures that AI Agents remain effective and relevant even as customer expectations and business environments evolve.
By integrating these capabilities, AI Agents can handle a wide range of tasks automatically, such as providing product recommendations, troubleshooting issues, and engaging in follow-up interactions. This automation frees human agents to focus on more complex, high-value activities.
Amazon’s Alexa is a notable example of an AI Agent. Integrated into devices like the Echo smart speaker, Alexa helps users perform various daily tasks via voice commands such as answering questions, setting alarms, playing music or controlling smart home devices namely lights or temperature settings. Additionally, Alexa assists users in online shopping, placing orders from Amazon, and creating to-do lists. It learns from user interactions to personalize the experience, such as recommending favorite products, songs, or reminders based on daily habit.

Benefits of Using AI Agents
In today’s context, delivering high-quality customer service is a critical factor for 83% of consumers when considering a purchase. However, 77% of businesses struggle to provide consistent customer experiences across different channels. AI Agents emerge as a crucial solution to this problem, offering the following four key benefits:
Improve Productivity and Efficiency
AI agents play a pivotal role in boosting productivity by automating repetitive and time-intensive tasks. This automation enables employees to dedicate their time to more strategic, creative, and high-value initiatives, fostering innovation and driving business growth. By streamlining operations, AI agents not only save valuable time but also allow businesses to allocate resources more effectively, resulting in improved efficiency across departments.
Moreover, AI agents excel in handling multiple tasks simultaneously, significantly enhancing operational efficiency. They are capable of managing large volumes of customer interactions without compromising service quality. For more complex issues, AI agents can intelligently escalate cases to human agents, ensuring they are directed to the most qualified team members. This seamless collaboration ensures smooth operations, even during periods of high demand.
Reduce Costs for business
One of the most impactful benefits of AI agents is their ability to significantly reduce operational costs. By minimizing human error and optimizing processes, they produce more with fewer resources. Their ability to handle complex tasks without constant supervision ensures that businesses can achieve their goals while keeping costs under control.
Scalability
As businesses grow, so do their customer support and operational needs. AI Agents are inherently scalable, able to manage increased volumes of interactions without compromising performance. This makes them ideal for businesses looking to expand while maintaining consistent service quality and operational efficiency.
Data-driven insights
By analyzing customer interactions and market trends, AI Agents generate actionable insights that help businesses refine their strategies. These insights enable companies to anticipate customer needs, improve service offerings, and stay ahead of the competition.
Enhanced customer experience
AI agents significantly enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty by offering round-the-clock support and personalized interactions. Their prompt and precise responses effectively address customer needs, ensuring a smooth and engaging service experience. By resolving issues and fulfilling requests promptly, AI agents help businesses cultivate stronger, more trusting relationships with their customers.
Lenovo harnessed the power of AI agents to transform its product configuration and customer service processes. By creating a comprehensive knowledge database from purchase data, product information, and customer profiles, the company successfully integrated AI agents into critical systems, such as inventory tracking tools.
Through collaboration among AI agents, Lenovo was able to reduce the average setup time from 12 minutes to just 2 minutes, resulting in a significant boost in sales team productivity and an improved customer experience. Key outcomes included a 12% increase in meeting the KPI of delivering orders within 17 days and an estimated value of $5.88 million generated in just one year, according to Gartner.

>>> Read more about: What is Generative AI? Trends in Applying GenAI from 2024 to 2027
Characteristics of an AI Agent
Autonomy
AI Agents can operate without direct human intervention, independently making decisions and executing actions. This capability enables AI Agents to handle complex tasks in real-time without requiring detailed step-by-step programming.
For example, in Tesla’s self-driving car system, AI Agents can adjust speed, change lanes, and stop based on sensor data regarding road conditions, obstacles, and other vehicles. In emergencies, the AI Agent can automatically brake or adjust the route without driver intervention. This demonstrates the high level of autonomy in the system, allowing vehicles to operate safely without human control.

Continuous Learning
AI Agents have the ability to continuously learn and improve by receiving feedback from their environment or external critiques. This feature helps AI not only perform tasks more effectively but also adapt to changes in its surroundings.
An illustration of this characteristic is a customer support chatbot that initially may only answer simple questions. However, through data gathered from customer interactions, it gradually learns to understand more complex queries and improve its responses. For instance, the Messenger chatbot has learned from millions of conversations, enabling it not only to grasp context but also to automatically offer more appropriate solutions to customers.
Reactive and Proactive
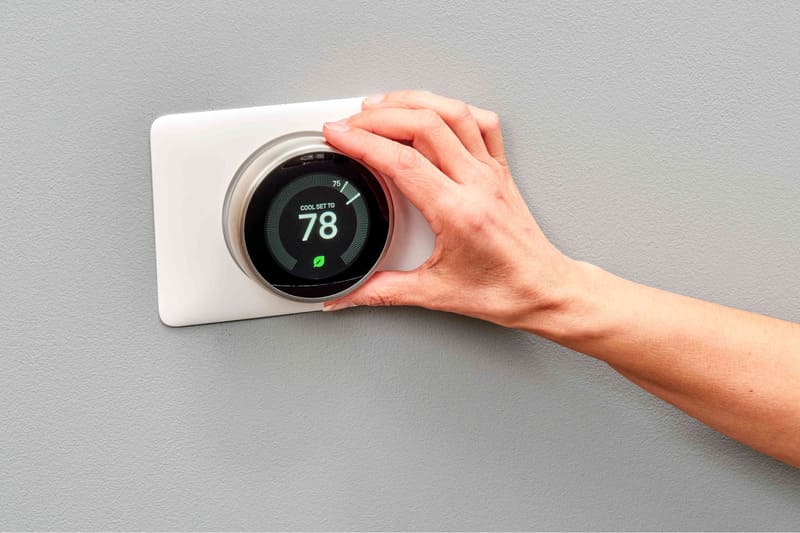
AI Agents not only respond to changes in their environment but also possess the ability to predict and take action before events occur. A detailed example of this characteristic can be observed in the Nest Thermostat, a smart temperature control device developed by Google.
The Nest Thermostat not only reacts to immediate temperature changes within a home but also learns from user habits and environmental factors to make predictive adjustments. For instance, after a period of use, the Nest Thermostat learns from user adjustments, noting when indoor temperatures rise due to midday sunlight or when to increase heating on cold mornings.
Moreover, the Nest Thermostat can react swiftly to sudden changes in the environment. If temperatures drop or rise too quickly, the system adjusts immediately to maintain comfort levels and save energy.

>>> Explore: What is an LLM Agent? How it works, advantages, and disadvantages
Popular Types of AI Agents
There are various types of AI agents, each designed for specific tasks and applications. Below are the key categories of AI agents:
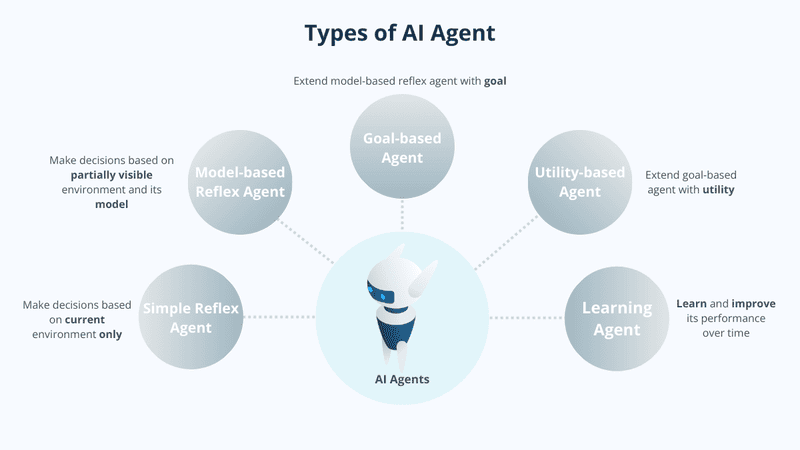
Simple Reflex Agents
Simple Reflex Agents operate based on the “condition-action” principle. They respond to the environment using pre-defined rules, such as a thermostat turning on the heating system at a specific time. These agents do not store any memory, cannot interact with other agents in the absence of information, and are not equipped to handle unexpected situations. Their responses are immediate and based on their current perception of the environment.
Model-Based Reflex Agents
Unlike simple reflex agents, Model-Based Reflex Agents maintain an internal model of the world. This enables them to retain information and adapt their behavior based on past interactions. These agents are capable of responding to dynamic environments, such as a vacuum cleaner robot that detects obstacles and adjusts its path. They also store information like areas already cleaned to avoid redundant tasks. While they can handle more complex situations, they are still limited by the rules they are programmed with.
Goal-Based Agents
Goal-Based Agents are designed to achieve specific objectives. They evaluate different actions to determine which ones will best help them reach their goals. These agents plan their actions in advance, considering the consequences of each step. For example, a navigation system suggests the fastest route to a destination by analyzing multiple possible routes. If a faster route becomes available, the system updates the suggestion accordingly.
Utility-Based Agents
Utility-Based Agents optimize outcomes by using a utility function, which measures the benefits of each action based on criteria such as time, progress towards a goal, or complexity. These agents make decisions by comparing the expected utility of various options to determine the most beneficial choice. For instance, a navigation system might consider factors like fuel consumption, travel time, and toll costs to recommend the best route.
Learning Agents
Learning Agents improve their performance over time by learning from interactions and feedback. They can adapt to new situations and continuously enhance their capabilities. These agents are especially useful in environments where they must deal with unfamiliar conditions. For example, e-commerce websites use Learning Agents to understand customer preferences and provide personalized product recommendations based on previous interactions.
Hierarchical Agents
Hierarchical Agents are organized in a layered structure. Higher-level AI agents oversee and direct lower-level agents to accomplish tasks that contribute to a common goal. This hierarchical setup is useful for breaking down complex processes into simpler, more manageable tasks. It allows each agent to focus on specific responsibilities, improving efficiency and collaboration within larger systems.
Each type of AI agent has its strengths and is suited to different scenarios, making it important to select the right agent for your specific needs. Whether you need a simple solution for repetitive tasks or a more sophisticated agent that can learn and adapt, understanding these different types of AI agents can help you leverage their capabilities effectively.
AI Agents Applications
AI agents are transforming a wide range of industries, providing innovative solutions and enhancing operational efficiency. Here are some examples of how AI agents are being integrated across various sectors, with specific use cases that demonstrate their versatility.
AI Agents in the Finance Industry
Delivering personalized customer service in finance is a challenge, but AI agents help bridge this gap. By analyzing unified customer data, AI agents offer valuable insights to human agents, enabling them to deliver tailored financial recommendations based on each customer’s specific needs and goals. Additionally, AI assists in preparing for client meetings by offering context-specific data.
AI agents also simplify the task of summarizing client interactions, which can often be error-prone and time-consuming. They can automatically generate summaries of open cases, orders, invoices, and recent activities, significantly saving time and reducing errors.
AI Agents in the Manufacturing Industry
AI agents play a crucial role in the manufacturing sector by monitoring machinery and predicting maintenance needs. This predictive capability helps avoid unplanned downtime and optimizes production processes, leading to improved productivity. Moreover, AI agents can assist sales teams by streamlining the sales pipeline, helping them close deals more effectively.
AI can also summarize sales agreements and highlight discrepancies between planned and actual quantities and revenues, enabling better-informed decisions that enhance profitability.
AI Agents in the Consumer Goods Industry
AI agents in the consumer goods industry are particularly beneficial for improving inventory management. They can compare expected and actual inventory at the end of each tour, adding context like whether items were included on trucks or referenced in original documents. This helps in keeping track of stock levels and streamlining inventory operations. Additionally, AI agents can simplify marketing campaign management by generating promotional content, ensuring customers stay informed about new products and company updates.
AI Agents in the Automotive Industry
For the automotive industry, AI agents provide a comprehensive view of vehicle or fleet performance. By analyzing vehicle telematics, AI can highlight urgent or critical alerts, enabling proactive maintenance and quick resolutions to issues. This contributes to improved fleet management and reduced operational costs. Automobile dealerships and repair shops can leverage AI agents for commerce, helping them quickly generate targeted promotions that resonate with their market.
AI Agents in the Healthcare Industry
In healthcare, AI agents are taking customer experience to the next level. Patient service agents can handle inquiries, schedule appointments with the most suitable physicians, review benefits, and approve care requests, ensuring that patients receive timely assistance. AI Agents can also help in building personalized treatment plans for patients, assist in managing medical records, and even match eligible patients to clinical trials based on their medical history and study criteria.
AI agents enhance the management of provider networks by allowing healthcare organizations to easily access and review provider information and past performance, ultimately reducing patient wait times and improving overall efficiency.

Challenges and Considerations When Using AI Agents
Although AI Agents are opening up groundbreaking potential in areas like automation, programming, and customer support, the technology is still in its infancy and faces significant challenges.
According to Kanjun Qiu, CEO and founder of the AI research startup Imbue, the development of AI Agents today can be compared to the race to develop self-driving cars a decade ago. While AI Agents can perform various tasks, they are not yet reliable enough and cannot operate entirely autonomously. One of the most significant issues AI Agents encounter is limitations in logical reasoning. As Qiu points out, AI programming tools can generate code, but they often write incorrect code or fail to test their outputs independently. This necessitates constant human intervention to refine processes.
Dr. Fan also notes that we have not yet reached a stage where AI Agents can fully automate daily repetitive tasks, as the systems still exhibit tendencies for “nonsense generation” and do not always adhere to user instructions precisely.

Another major limitation is the context window—the ability of AI models to read, understand, and process large volumes of data. Dr. Fan explains that models like ChatGPT can handle programming but struggle with long and complex code segments, whereas humans can easily follow hundreds of lines of code without difficulty. Companies like Google have had to enhance context processing capabilities in their AI models, such as with the Gemini model, to improve performance and accuracy.
For AI Agents with physical forms, like robots or virtual characters in games, training them to perform human-like tasks also poses a challenge. Currently, the data available to train such systems is limited, and research is only beginning to explore how generative AI can be applied to automation.
Building AI Agent Teams: A Key Technology Trend for 2025
According to Gartner, AI Agents top the list of strategic technology trends for the coming year. The organization also predicts that by 2028, at least 15% of daily work decisions will be automated by AI Agents. Moreover, Insider reports that the AI Agents market, valued at $3.7 billion in 2023, is expected to reach $103.6 billion by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 44.9% from 2024 to 2032.
The value AI Agents bring to businesses lies in their ability to automate a wide range of complex use cases, saving both costs and time. Common tasks supported by AI Agents include software development, automated customer support, business operations, cybersecurity, and risk detection.

Recognizing this trend, many companies have begun building their own AI Agent teams. For example, in 2023, FPT Long Chau partnered with FPT Smart Cloud to establish an AI Agent workforce to support pharmacist training—those who are the front-line employees interacting directly with customers. The training materials for more than 16,000 pharmacists across 2,000 pharmacies were personalized through FPT AI Mentor.
Enhancing pharmacists’ competencies contributed significantly to FPT Long Châu’s business operations. Within the first nine months of the year, the pharmacy chain recorded a revenue growth of 62%, reaching VND 18.006 trillion, accounting for 62% of FRT’s total revenue and completing 85% of its 2024 plan.
According to the global consulting group IMARC, Vietnam’s AI market reached a value of USD 547.1 million in 2023 and is projected to soar to USD 2.06 billion by 2032, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.8%.
Vietnamese tech giants have been aggressively investing in the race to develop AI Agents. Notably, FPT Group announced the launch of two AI factories (FPT AI Factory) in Japan and Vietnam in November. Additionally, FPT Smart Cloud (a subsidiary of FPT Group) introduced FPT AI Agents, a platform for creating and managing multilingual AI Agents in English, Vietnamese, Japanese, and Indonesian.

With this technological advancement, businesses can create their own AI Agents within minutes or hours. These AI Agents stand out with unique personalities and characteristics, as they are developed based on the specific Data and Culture of each organization. This differentiation fosters a completely new competitive edge among enterprises and extends to building AI sovereignty among nations.
Built on the robust infrastructure of FPT AI Factory, FPT AI Agents promise significant breakthroughs in operational efficiency, exceptional customer experiences, and unlimited creative potential for all businesses.
Learn more about the FPT AI Agents platform at: https://fpt.ai/products/fpt-ai-agents-en/